How to setup an OpenShift container group with AAP
Ansible Automation Platform Container Groups
AAP Container Groups is just like Instance Groups. However, the playbooks will be executed in a pod running in your OpenShift or Kubernetes environment. You can find the details at Container and Instance Groups
What if you want to test this out but don’t have access to an OpenShift or Kubernetes environment? Here is an example how I set one up using the free Red Hat OpenShift sandbox to create a Container Group in my AAP environment.
Create an OpenShift service account
Login to https://developers.redhat.com to sign up for a sandbox instance. Once the instance is up, login with you developer credential. You should see two projects/namespaces. Let’s use the -dev project. We will create a service account aap-sa and a role aap-sa-role. They will be binded with rolebinding aap-sa-role-binding to the echong-2-dev project. Save the following to file aap-sa.yml.
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: aap-sa
namespace: echong-2-dev
spec:
serviceAccountName: aap-sa
---
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aap-sa-role
namespace: echong-2-dev
rules:
- apiGroups:
- ""
resources:
- pods/exec
- pods/attach
- pods
- secrets
verbs:
- get
- list
- watch
- create
- delete
- update
---
kind: RoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: aap-sa-rolebinding
namespace: echong-2-dev
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: aap-sa
namespace: echong-2-dev
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: aap-sa-role
Create this service account and role by running
oc apply -f aap-sa.yml -n echong-2-dev
Two tokens will be generated with the service account. Obtain the token string by running
oc sa get-token aap-sa
Save the token string for the next step.
Create an AAP Credential
On AAP controller, create a OpenShift or Kubernetes API Bearer Token type credential. Enter the OpenShift Sandbox endpoint and the Service Account token string from previous step.
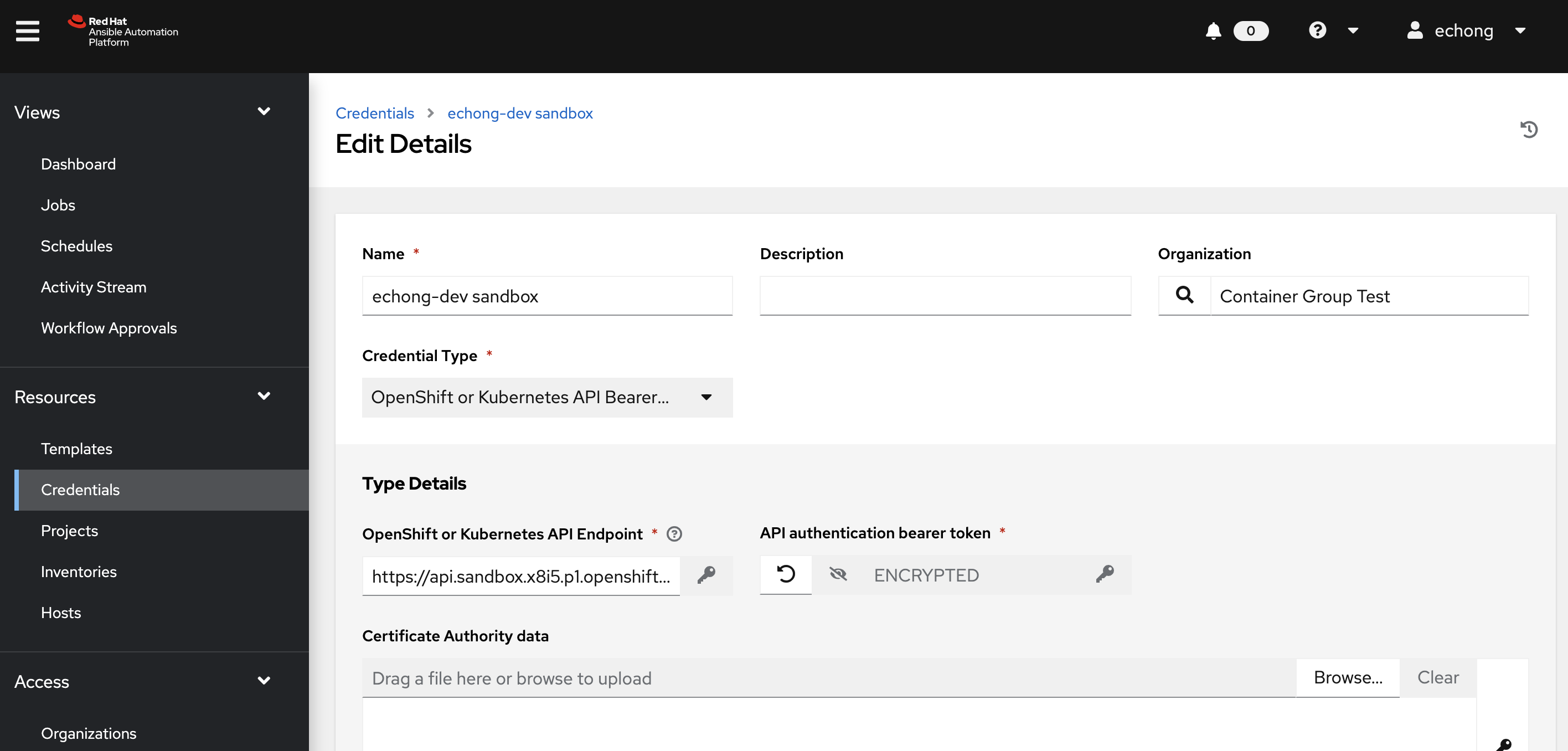
Create an AAP Container Group
On AAP controller, create a Container Group under the Instance Groups menu. Use the OpenShift credential created in previous step. Select Customize pod specification to make some additional modification.
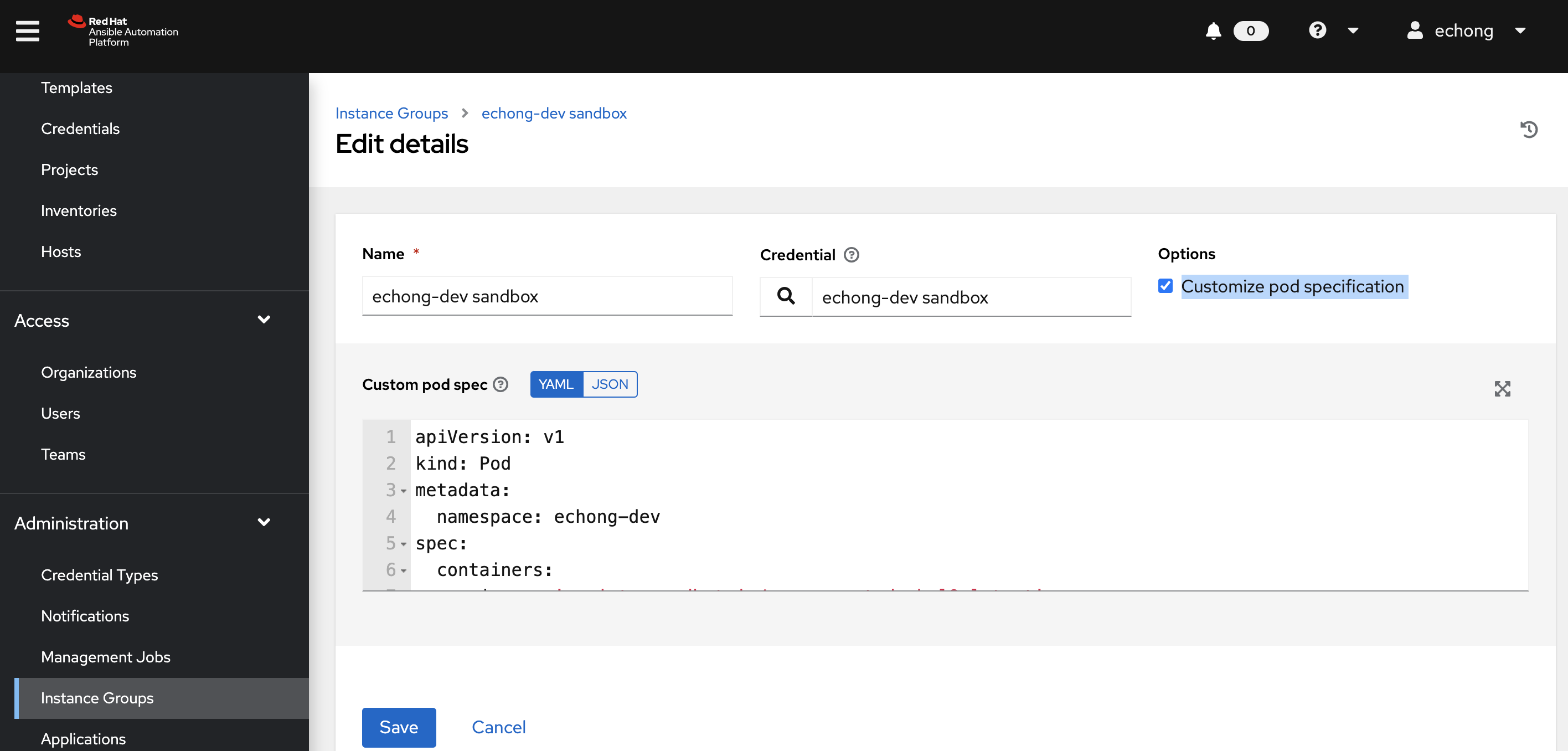
The default settings will try to pull the execution environment from your Automation Hub and use the default namespace. Remove the image line which is actually not used. The image is determined by the execution environment specified in the template. Change the namespace to one of the projects created for you in the sandbox. Add the service account created in step above.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
namespace: echong-2-dev
spec:
serviceAccount: aap-sa
containers:
- name: worker
args:
- ansible-runner
- worker
- '--private-data-dir=/runner'
That’s it. Launch a playbook against an inventory that is reachable on the internet, since the execution environment is running in the cloud. Make sure the job/workflow template is using the container group we created as Instance Group. We still need to specify an execution environment that is publicly accessible. Try to use Default execution environment which is pointing to registry.redhat.io.
Custom Execution Environment
What if the default execution environment is not enough and we need to run it with a custom EE from a private repo on Quay.io?
First update the Custom pod spec for the Container Group to include an imagePullSecrets.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
namespace: echong-2-dev
spec:
serviceAccount: aap-sa
imagePullSecrets:
- name: echong-aap-test-quay.io
containers:
- name: worker
args:
- ansible-runner
- worker
- '--private-data-dir=/runner'
Next create this imagePullSecrets on the OpenShift Sandbox using a robot account generated for the repo on Quay.io.
oc create secret docker-registry \
--docker-server=quay.io \
--docker-username=<robot account name> \
--docker-password=<robot account token> \
echong-aap-test-quay.io -n echong-2-dev
Create a new Execution Environment to point to the custom image on Quay.io accesible from this robot account.
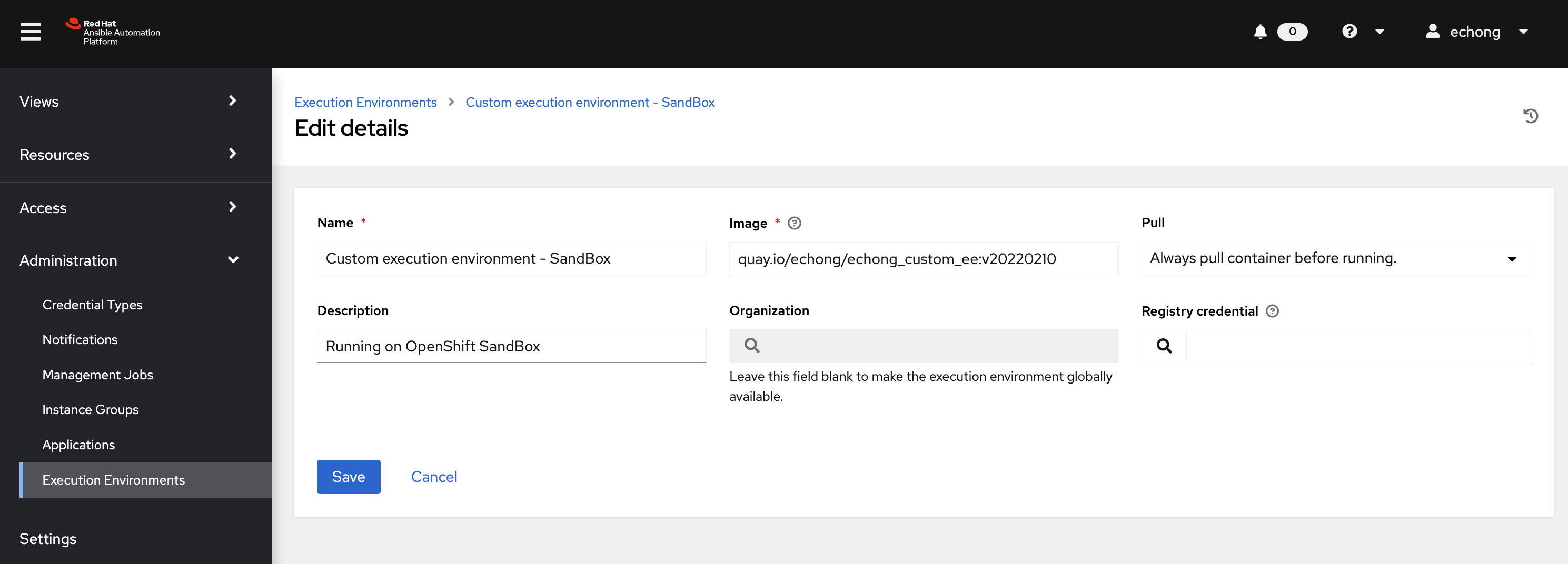
Last step is to update the Job Template using the OpenShift Sandbox Container Group to use this execution environment. Now lauch the template and a new pod will be deployed on the Sandbox and using your customer execution environment from Quay.io.
P.S. While writing this, Ansible blog @ ansible.com/blog pusblished a similar article. Please check that out too!
Leave a comment